Posted
8th June 2023
Research
In today’s blog, we’ll be discussing a new publication from the Journal of Hospital Infection. In a world first, researchers have evaluated and concluded the impact of detergent-disinfectant wipes on patient outcomes, including in-hospital mortality[1].
The ultimate goal of any IPC practice, including environmental decontamination, is to help save lives; for the first time, researchers have endeavoured to prove just that.
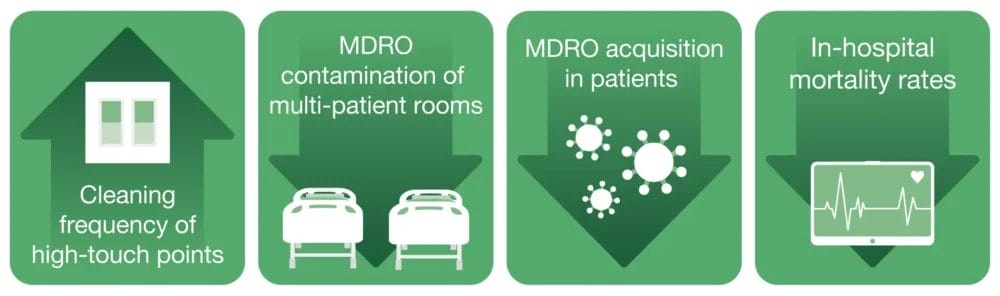
When researchers from Israel’s Shamir Medical Centre replaced their traditional chlorine-based protocol with a simple 2-in-1 wipe (Clinell Universal Wipes), they demonstrated:
Like many healthcare organisations, Shamir Medical Centre used a 1,000ppm chlorine solution to disinfect surfaces, along with multi-use buckets and cloths.
Effective environmental decontamination requires 2 steps
Chlorine’s critical flaw is that it has no cleaning properties and is inactivated by organic matter[2] – making it unsuitable for removing dirt or bodily fluids without a pre-cleaning step.
An effective environmental decontamination protocol should factor in both steps required to make surfaces safe: cleaning and disinfection.
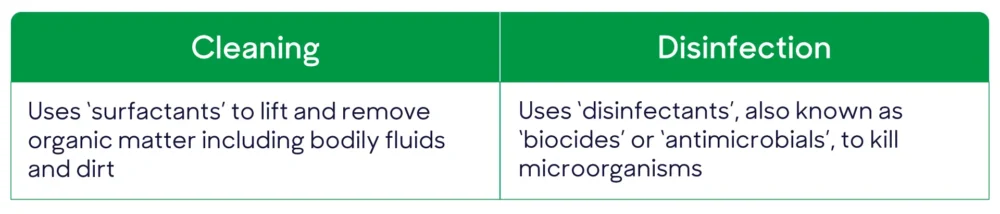
Clinell Universal Wipes contain both elements and benefit from a combination of biocides which enhance their antimicrobial performance.
Building a breakthrough trial
From October 2016 to January 2018, 4 medical departments participated in a crossover trial. For 6-month periods, they randomly adopted one of two environmental decontamination protocols before swapping to the alternative:
- Control – Chlorine solution (1,000ppm) plus multi-use buckets and cloths
- Intervention – Clinell Universal Wipes placed in a dispenser at patients’ bedsides

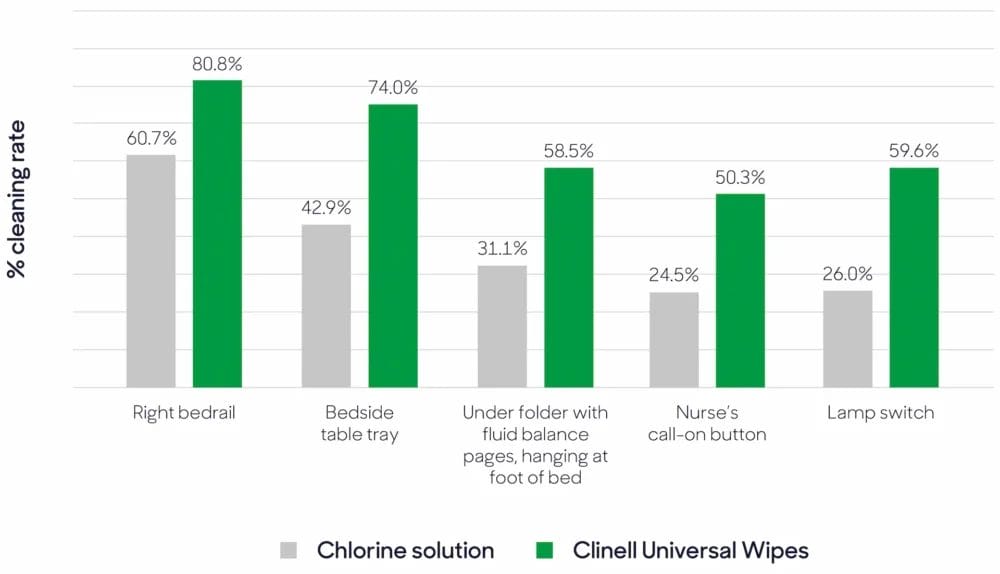
5 high-touch points audited using Clinell EvaluClean.
Image source: Dadon et al. J Hosp Infect. 2023;134:50-56.
Placement is important
In real-world healthcare settings, multi-patient wards are full of life. Healthcare workers are challenged with juggling patient care and high standards of environmental decontamination.
As well as a simple product, strategic placement helps ensure that decontamination is undertaken at the moment that matters. In the direct eye line of busy healthcare workers, the dispenser acts as a visual reminder and removes the time taken to locate multiple products.

Results showed that placing wipes at patients’ besides improved environmental cleaning frequency by 33.6%. In some instances, the frequency of cleaning nearly doubled with the implementation of the Clinell Universal Wipe and dispenser protocol.
Wipes impact patient safety
The study observed the acquisition rates of MDROs within each ward, looking specifically at the most epidemiologically significant human pathogens, including MRSA, VRE, CRE, A.baumannii, and P. aeruginosa.
Across each pathogen, the Clinell protocol was found to reduce MDRO acquisition rates. This observation aligns with other findings, which have shown significant reductions in other significant pathogen acquisitions, such as a 55% reduction in MRSA documented by Garvey et al in the Journal of Hospital infection[3].
Importantly, this new study is the first to measure and conclude the impact of wipes on patient survival. For the first time, the implementation of Clinell Universal Wipes has been proven to contribute towards reduced in-hospital mortality rates as part of a holistic environmental decontamination strategy.
This finding demonstrates the positive impact of introducing a simple and time-saving[4] protocol on patient outcomes.
Consider a simplified protocol
Reflecting on this ground-breaking study, there is sufficient evidence to support the use of detergent-disinfectant wipes in place of chlorine solutions. Replacing chlorine solutions with Clinell Universal Wipes and dispensers:
- Improves cleaning and disinfection of high-touch points
- Reduces environmental contamination
- Reduces pathogen acquisition
- Improves outcomes in healthcare
Researchers concluded: ‘This is a feasible, recommended practice to improve patient outcomes in multi-patient rooms’.
As Infection Prevention and Control Teams strive to improve patient care, this simple, practical solution could be the key to unlocking their success.
[1] Dadon M, Chedid K, Martin ET, et al. The impact of bedside wipes in multi-patient rooms: a prospective, crossover trial evaluating infections and survival. J Hosp Infect. 2023;134:50-56. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2022.11.025
[2] Rutala WA, Weber DJ. Uses of inorganic hypochlorite (bleach) in health-care facilities. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997;10(4):597-610. doi:10.1128/CMR.10.4.597
[3] Garvey MI, Wilkinson MAC, Bradley CW, Holden KL, Holden E. Wiping out MRSA: effect of introducing a universal disinfection wipe in a large UK teaching hospital. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018;7(1):155. doi:10.1186/s13756-018-0445-7
[4] Shepherd E, Leitch A, Curran E. A quality improvement project to standardise decontamination procedures in a single NHS board in Scotland. J Infect Prev. 2020;21(6):241-246. doi:10.1177/1757177420947477
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Tags
Latest News
Norovirus: Understanding its transmission and prevention in the UK
Introduction Norovirus is recognised as the leading cause of viral gastroenteritis…
Clean Between to Reduce Healthcare-Associated Infections
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) are a significant concern for healthcare facilities…
Mpox: emergence of a new threat
A new threat related to mpox is emerging, in the…
Wiping away infections – the CLEEN way!
Cleaning shared medical equipment with a disinfectant wipe at least…