Posted
7th February 2018
Research
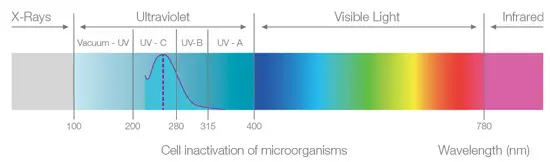
A US study has found that Candida auris exhibited a similar level of susceptibility to UV light as Clostridium difficile spores, and was considerably less susceptible than MRSA. These findings suggest that either extended exposure UV cycles or hydrogen peroxide based room disinfection are required to address environmental contamination with Candida auris.
We have posted before on the efficacy of various disinfectants against Candida auris, supporting that chlorine-based disinfectants and chlorhexidine have a role to play in preventing the transmission of Candida species. This latest laboratory study tested the efficacy of a UV room decontamination system against various species of Candida auris and Candida albicans, MRSA, and C. difficile spores. Metal discs with these organisms dried onto them were placed 5 feet from the device at a height of 4 feet with exposure times of 10, 20, or 30 minutes. UV achieved a <2-log reduction on C. auris after 10 minutes of exposure (vs. a >6-log reduction for MRSA), a 4-log reduction after 20 minutes, and a 6-log reduction after 30 minutes. The efficacy profile of UV against C. difficile and C. auris was similar.
This study is in line with the findings of others that C. auris is able to less susceptible to disinfection than other agents. Therefore, extended exposure UV cycles or hydrogen peroxide based room disinfection should be used to tackle environmental contamination with C. auris.
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Tags
Latest News
Embracing sustainability and cost savings: The journey of Clinell Indicator Notes to paper-based solutions
At GAMA Healthcare, we’ve always prided ourselves on being at…
Introducing HEXI HUB: A seamless transition in our product line
We’re pleased to announce an update to our product offering…
Innovative solutions for tackling Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) at King’s College Hospitals
King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, one of London’s largest…
Gloves Off: reducing unnecessary plastic waste during environmental cleaning and disinfection
In this blog, Dr Phil Norville discusses the momentum-gaining ‘Gloves…