Posted
28th September 2022
Research
Today on the blog, we discuss endospores in healthcare, sporicidal EN testing and how effective Clinell Peracetic Acid Wipes really are.
Endospores in healthcare
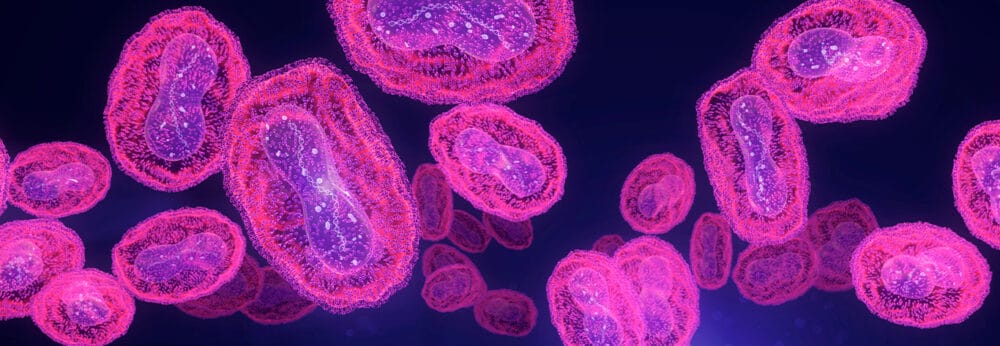
Bacteria utilise a wide variety of defence mechanisms when facing extreme environmental conditions. Certain Gram-positive bacteria produce intracellular spores called endospores, which prove a complex challenge for healthcare settings and infection prevention in general. These endospores are incredibly tolerant to environmental pressures such as temperature, UV, antibiotics and biocides.
Bacterial endospores are metabolically inactive. However, when conditions return to a favourable state, the endospore will begin germination and, as a result, return to a vegetative cell form, which is metabolically active and able to cause active infection. Understanding the sporulation/germination cycle is vital for testing and identifying adequate sporicidal biocides.
Sporicidal effect of biocides
Biocidal products (disinfectants, antimicrobials, etc.) are strictly regulated to guarantee safe use, conditions, and performance. Laboratory assessments of biocidal products must be performed to support and validate product claims. These assessments must be done following recognised international or national tests with a standard methodology to examine the efficacy of disinfectants.
Peracetic acid (PAA) is one of a small number of chemical biocides that are actively sporicidal. PAA is a strong oxidiser with broad-spectrum antimicrobial efficacy against bacteria, yeast, fungi, non-enveloped viruses and spores. Its use in disinfection products ensures the reduction of spores within a short contact time, which can even be achieved at low temperatures.

EN testing and standards for disinfection
The European Committee for Standardisation (CEN) produced harmonised European methods (EN tests) for testing the activity of disinfectants used in various settings, including medical, veterinary, food, industrial, domestic and institutional areas. EN tests are categorised into:
- Suspension test (Phase 1, Phase 2, Step 1)
- Surface tests (Phase 2, Step 2)
- Field Trial tests (Phase 3)
A biocidal product should be assessed following the most relevant test according to the area or intention of use (medical, veterinary and food hygiene). EN tests are constantly being developed, improved, and updated so that products meet the requirements within realistic conditions and contact times. However, if no test method is available, a test from another area can be used instead while adapting the parameters accordingly.
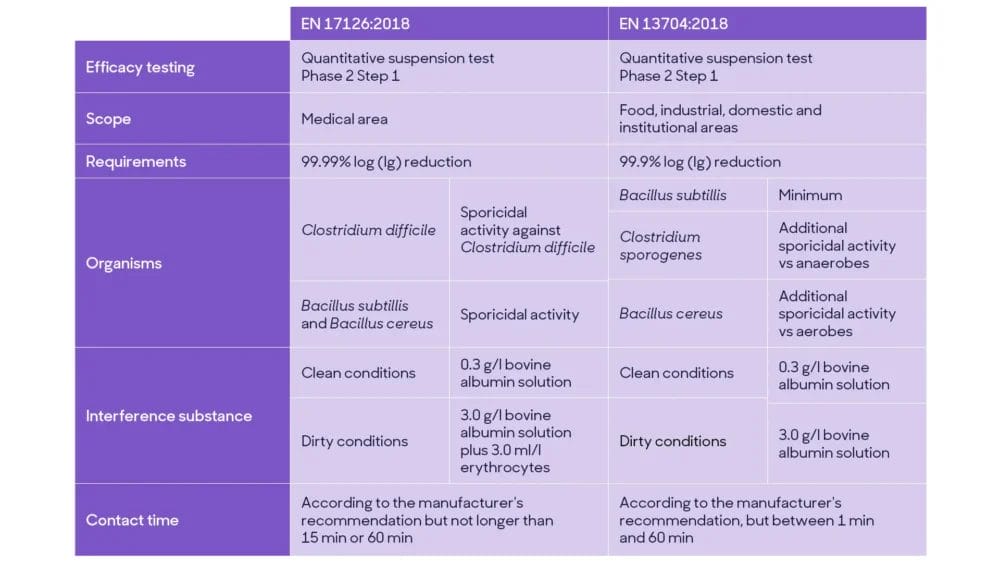
Current EN tests for sporicidal activity, such as EN 13704:2018 and EN 17126:2018, are quantitative suspension tests (Phase 2, step 1). Overall, they simulate practical conditions according to intended product use, temperature, contact time and interfering substances.
Sporicidal EN testing
Currently, there are two EN test methods available for sporicidal claims:
EN 17126 provides instructions on evaluating sporicidal efficacy against Clostridium difficile and against Bacillus subtillis & Bacillus cereus, requiring a 4 Log reduction as pass criteria in clean and medical dirty conditions.
EN 13704 specifies the requirements for sporicidal activity of chemical products used in food, industrial, domestic and institutional areas, with a pass criterion of 3 log reduction.
The main difference between the EN sporicidal methods include the product’s area of use, pass criteria, microorganisms tested, conditions (interference substances) and contact time. At the same time, EN 17126 is more stringent and relevant for sporicidal products intended to be used in medical settings.
Clinell Peracetic Acid Wipes

Clinell Peracetic Acid Wipes utilise a patented technology to combine the efficacy of peracetic acid and hydrogen peroxide that uses oxidative reactions to break through a spore’s coats to inactivate the spore underneath.
Following EN 17126:2018, Clinell Peracetic Acid Wipes are proven to have sporicidal activity under dirty conditions against Clostridium difficile in 2 min and Bacillus subtills and Bacillus cereus in 2 and 5 min, respectively.
Clinell Peracetic Acid Wipes are also effective against microorganisms less susceptible to biocides such as non-enveloped viruses, mycobacteria, and bacterial spores.
If you’d like more efficacy data on our Clinell Peracetic Acid Range, please drop us a line on info@gamahealthcare.com and one of our team will be in touch. Help spread the word by sharing this article on social media.
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Tags
Latest News
Norovirus: Understanding its transmission and prevention in the UK
Introduction Norovirus is recognised as the leading cause of viral gastroenteritis…
Clean Between to Reduce Healthcare-Associated Infections
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) are a significant concern for healthcare facilities…
Mpox: emergence of a new threat
A new threat related to mpox is emerging, in the…
Wiping away infections – the CLEEN way!
Cleaning shared medical equipment with a disinfectant wipe at least…